Services
type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition where the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. Common symptoms include frequent urination, increased thirst, and unexplained weight loss. Risk factors include obesity, inactivity, genetics, and poor diet. Management involves lifestyle changes, medications, and regular monitoring to prevent complications like heart disease, nerve damage, and kidney problems.
Thyroid disorders
Thyroid disorders affect hormone production, causing conditions like hyperthyroidism (excess) and hypothyroidism (deficiency). Symptoms include weight changes, fatigue, and sensitivity to temperature. Causes may include autoimmune diseases like Graves’ or Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Treatment involves medications, radioactive iodine, or surgery to restore normal hormone levels and manage symptoms effectively. Regular monitoring is essential for ongoing management.
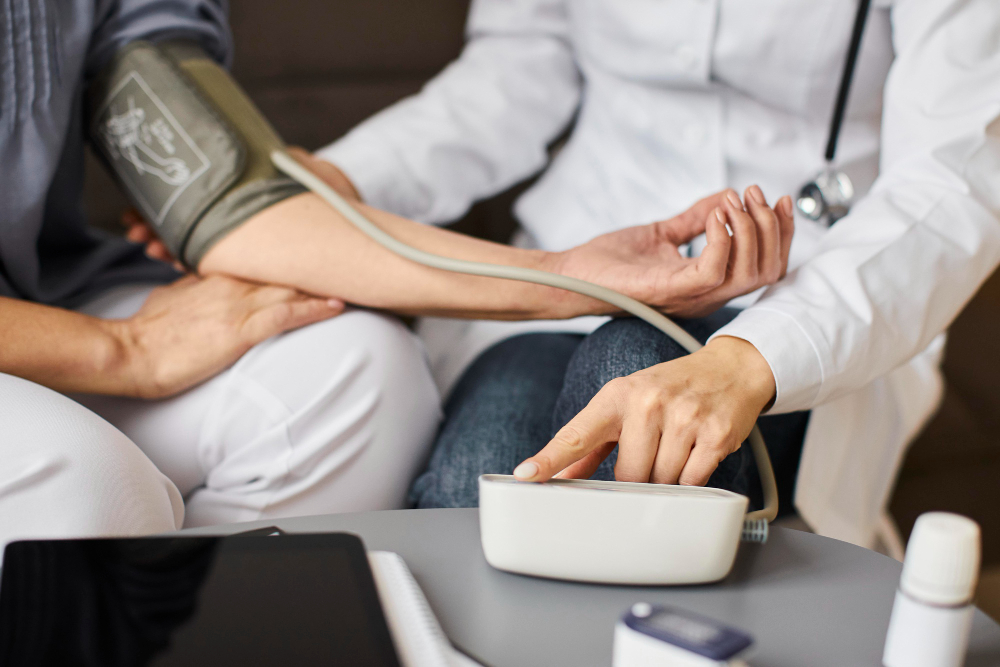

hypertension
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a chronic condition where the force of blood against artery walls is too high. Often asymptomatic, it can lead to serious health issues like heart disease, stroke, and kidney damage. Risk factors include obesity, smoking, excessive alcohol, and high salt intake. Management involves lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, along with medications to control blood pressure levels.

Tropical infections and Infectious diseases
Tropical infections and infectious diseases are illnesses prevalent in tropical and subtropical regions, caused by bacteria, viruses, parasites, and fungi. Common diseases include malaria, dengue, chikungunya, and Zika. These diseases often spread through vectors like mosquitoes or contaminated water and food. Symptoms vary widely but can include fever, chills, and muscle aches. Prevention involves vector control, vaccination, and proper hygiene, while treatment depends on the specific pathogen involved.

autoimmune disorder
Autoimmune disorders occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues, considering them foreign. Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis result from this abnormal response. Symptoms vary but often include fatigue, inflammation, pain, and tissue damage. Risk factors include genetics, infections, and environmental triggers. Management focuses on reducing symptoms and controlling the immune response through medications, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring.

Arthritis
Arthritis is a group of conditions causing inflammation and pain in the joints. Common types include osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Symptoms include joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and reduced mobility. Risk factors are age, genetics, injury, and obesity. Treatment aims to relieve symptoms and improve joint function through medications, physical therapy, lifestyle changes, and, in severe cases, surgery. Regular exercise and a healthy diet can help manage the condition.

Poisoning cases
Poisoning cases occur when harmful substances, such as chemicals, drugs, or plants, are ingested, inhaled, or absorbed, leading to toxic effects. Symptoms vary widely, including nausea, vomiting, confusion, or difficulty breathing. Immediate treatment involves removing the toxin, supportive care, and specific antidotes if available. Prevention includes proper storage of chemicals, cautious use of medications, and awareness of potential poisons. Prompt medical attention is crucial for effective treatment.
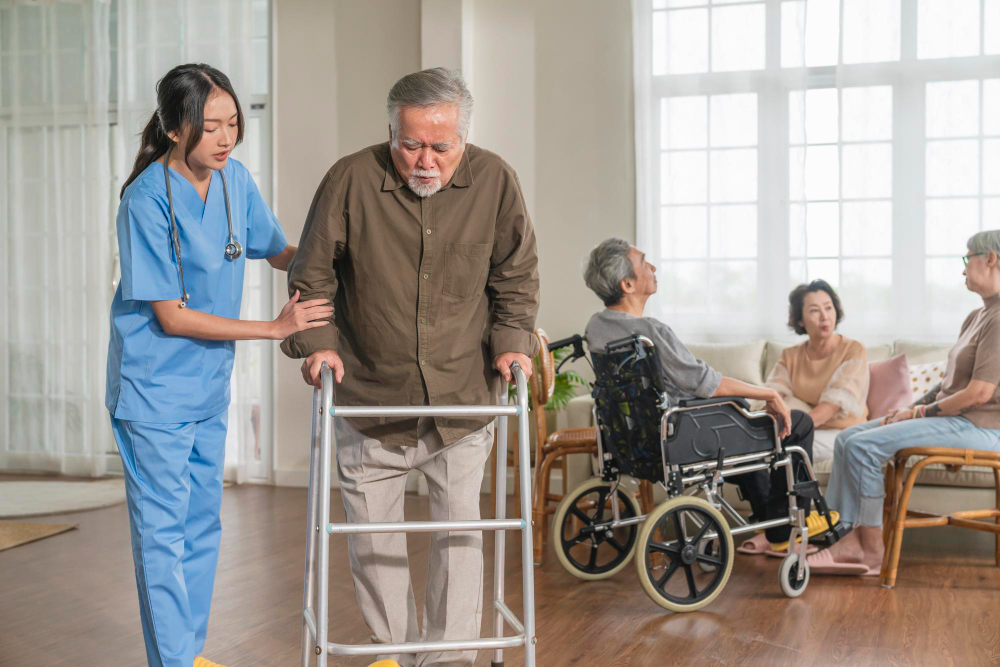

Geriatric care
Geriatric care focuses on the health and well-being of older adults, addressing age-related issues such as chronic diseases, mobility problems, and cognitive decline. It involves a multidisciplinary approach to manage conditions like arthritis, diabetes, and dementia. Key aspects include preventive care, personalized treatment plans, medication management, and support for daily activities. The goal is to enhance quality of life and maintain independence while addressing the unique needs of elderly patients.

Medical disorders in pregnancy
Medical disorders in pregnancy include conditions like gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and hyperemesis gravidarum. These disorders can impact both maternal and fetal health, leading to complications such as high blood pressure, excessive vomiting, and abnormal blood sugar levels. Early diagnosis and management are crucial for minimizing risks. Treatment may involve lifestyle changes, medications, and regular monitoring to ensure a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
critical care
Critical care involves the management of patients with severe, life-threatening conditions requiring intensive monitoring and treatment. It includes care for those with multi-organ failure, severe infections, trauma, and post-surgical complications. Critical care teams use advanced technology and therapies to stabilize patients, manage vital functions, and provide supportive care. The goal is to improve outcomes and recovery through continuous monitoring and personalized treatment plans in specialized units.

Obesity
Obesity is a condition characterized by excessive body fat accumulation, often measured by a high Body Mass Index (BMI). It increases the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and hypertension. Causes include poor diet, lack of physical activity, and genetic factors. Management involves lifestyle changes like a balanced diet and regular exercise, along with medical treatments or surgery in severe cases, to improve overall health.

Nutritional Problem
Nutritional problems arise from imbalances in nutrient intake, leading to deficiencies or excesses that impact health. Common issues include malnutrition, obesity, and vitamin or mineral deficiencies. Causes can be poor diet, digestive disorders, or socioeconomic factors. Symptoms vary from fatigue and weakness to more severe health complications. Management includes dietary adjustments, supplementation, and addressing underlying causes to restore nutritional balance and improve overall well-being.

